In the world of blockchain technology, consensus mechanisms are crucial to maintain the network’s security and integrity. One of the most popular consensus mechanisms used by blockchain networks is Proof of Stake (PoS). PoS is an energy-efficient alternative to the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin.

Table of Contents
What is Proof of Stake?
Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanism used by blockchain networks to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Unlike PoW, where miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems to add new blocks to the blockchain and earn rewards, PoS relies on validators to secure the network.
Validators are individuals or entities that hold a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral to become a validator. Validators are selected based on their stake in the network and the amount of cryptocurrency they hold. The more cryptocurrency a validator holds, the higher their chances of being selected to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain.
How Does Proof of Stake Work?
In a PoS blockchain network, validators are responsible for creating and validating new blocks. To become a validator, an individual or entity needs to hold a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral, which is called a stake. The higher the stake, the higher the chance of being selected to create and validate new blocks.
Once a validator is selected, they create a new block and validate transactions. Validators are incentivized to act in the network’s best interest as they risk losing their stake if they behave maliciously or act against the network’s rules. Validators are rewarded for their services in the form of cryptocurrency. The reward is proportional to the validator’s stake in the network.
Benefits of Proof of Stake
PoS offers several benefits compared to PoW. Here are some of the benefits of PoS:
- Energy Efficiency
PoS is more energy-efficient than PoW as it doesn’t require miners to solve complex mathematical problems. Validators only need to hold cryptocurrency as collateral, which consumes significantly less energy. - Security
PoS contributes to the network’s security by incentivizing validators to act in the network’s best interest. Validators are rewarded for their services, which motivates them to maintain the network’s integrity. - Decentralization
PoS promotes decentralization by allowing anyone to become a validator by holding a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral. This makes the network more resilient and resistant to centralization. - Accessibility
PoS is more accessible than PoW as it doesn’t require expensive hardware or technical expertise. Anyone can become a validator by holding cryptocurrency as collateral.
What are the Staking Platforms?
Staking Platforms are Validators on the PoS blockchain: nodes with a large amount of cryptocurrency. Their function is to validate transactions on the blockchain and create new blocks. In PoS, the probability of being selected as a validator is proportional to the amount of cryptocurrency one holds. In other words, the more cryptocurrency one holds, the greater the probability of becoming a validator.
Staking platforms are companies that allow cryptocurrency holders to stake on the PoS blockchain without having to manage a staking node themselves. They offer paid staking services, where users deposit their cryptocurrency on the platform and the platform becomes a staking node on the PoS blockchain. This way, users do not have to worry about managing the node and still receive a percentage of interest on their staked cryptocurrency.
Staking platforms also offer greater accessibility to cryptocurrency holders who do not possess the required amount of cryptocurrency to become a validator. Additionally, staking platforms can manage the risks associated with validating transactions on the PoS blockchain, such as the loss of cryptocurrency due to hacker attacks or node malfunctions.
How to stake cryptocurrencies?
Staking cryptocurrencies is a great way to earn passive income and support the blockchain network’s security. This is a step-by-step guide to learn how to stake cryptocurrency:
1. Choose a cryptocurrency to stake
The first step in staking cryptocurrencies is to choose a cryptocurrency that supports staking. Some of the popular cryptocurrencies that support staking include Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL), Cardano (ADA), Cosmos (ATOM), Polkadot (DOT).
2. Set up a Wallet
To stake cryptocurrencies, you need to have a wallet that supports staking. Some of the popular wallets that support staking are MetaMask, Ledger, and Trezor, but you can also use exchange wallets such as Binance, Kraken or Coinbase. For security reasons, it is not advisable to store large amounts of cryptocurrency in exchange wallets.
3. Find a Staking Platform
When selecting a crypto staking platform, it’s essential to prioritize the security and reputation of the platform. Look for platforms that have a strong track record of reliability and employ robust security measures to protect your funds. Make sure you fully understand the fees, rewards, and the process for withdrawing funds before committing your investment. Consider the types of cryptocurrencies supported by the platform and the potential rewards for staking each one.
4. Stake your Cryptocurrency
Once you have chosen a staking platform, the next step is to stake your cryptocurrency. The process of staking varies from platform to platform, but it generally involves locking your cryptocurrency in a staking pool for a certain period. Generally, depending on the cryptocurrency, there are minimum waiting times to allow funds to be released and staking to be canceled, should the need arise. You will continue to receive rewards until you start the unstaking process.
5. Monitor your Staking Rewards
After staking your cryptocurrency, you can monitor your staking rewards on the staking platform or your wallet. Staking rewards are usually paid out in the form of the cryptocurrency you staked, and the amount of rewards you receive depends on the staking platform’s reward distribution policy and fees.
Here are some tips to keep in mind while staking cryptocurrencies, Crypto Education is really important in the Web3 space:
- Choose a staking platform that has a good reputation and offers competitive staking rewards.
- Make sure to understand the staking platform’s terms and conditions before staking your cryptocurrency.
- Diversify your staking portfolio by staking different cryptocurrencies on different platforms.
- Keep your cryptocurrency in a secure wallet and never share your private keys with anyone.
- Monitor your staking rewards regularly to ensure you are receiving the expected returns.
Ethereum (ETH) Staking
Ethereum (ETH) uses the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. To become a validator node on the Ethereum blockchain and participate in staking, there are requirements that must be met.
Firstly, a validator node must hold a minimum of 32 ETH. This is known as the “staking threshold” and is required to ensure that validators have a significant stake in the network and are incentivized to act in the best interest of the network. Additionally, validator nodes must have a stable internet connection and be able to run the necessary software.
To become a validator node, one must first download and set up the Ethereum 2.0 client software. There are several software clients available, including Prysm, Lighthouse, and Teku. Once the software is installed and configured, the validator node can be activated by depositing 32 ETH into the Ethereum 2.0 deposit contract. The deposit contract is a smart contract on the Ethereum blockchain that holds the staked ETH and manages the validator node’s participation in staking.
These agencies pool together the staked ETH from multiple clients and operate a validator node on behalf of their clients. In return, clients receive a percentage of the staking rewards based on their contribution to the pool.
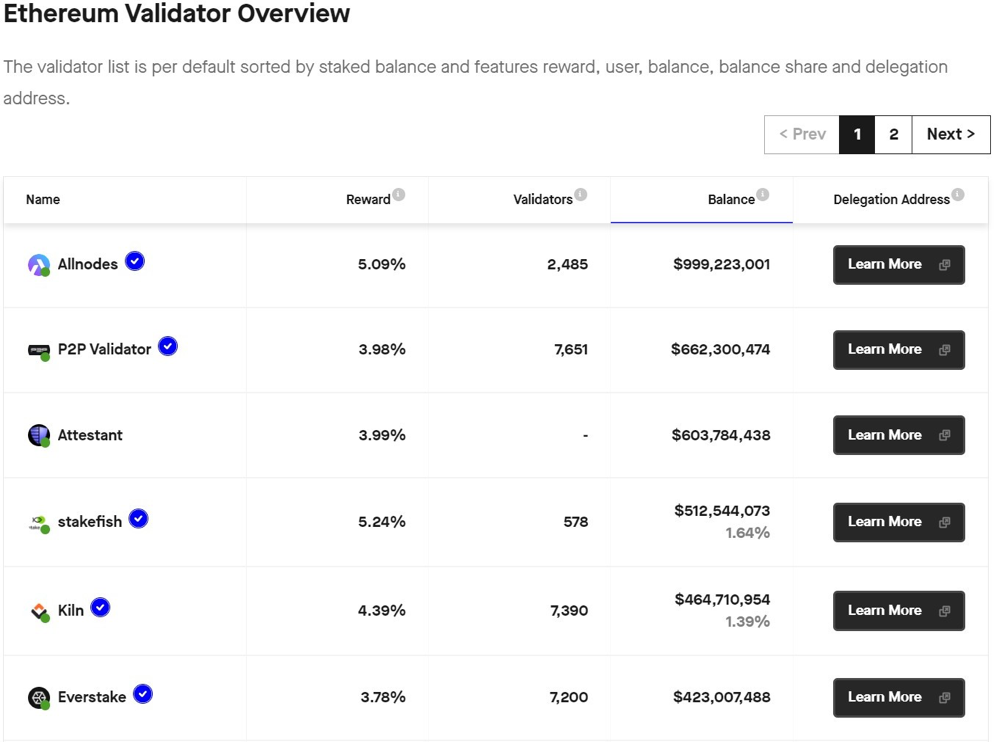
In addition to the centralized solutions of the most popular Exchanges, decentralized staking solutions can also be used:
- Rocket Pool – It is a decentralized staking platform that allows users to pool their ETH and stake it as a single entity. It operates with a network of nodes that are incentivized to ensure maximum security and uptime for the platform. Users can deposit any amount of ETH into Rocket Pool and receive rETH, which represents their staked ETH in the pool.
- Lido – It is a decentralized staking platform that allows users to stake their ETH without having to run their own validator node or hold the minimum staking threshold of 32 ETH. Lido operates a network of nodes that are responsible for staking users’ ETH and distributing staking rewards back to users in the form of stETH, which represents their share of the pool.
- StakeWise – It is a decentralized staking platform that allows users to stake any amount of ETH, regardless of whether they meet the minimum staking threshold of 32 ETH. StakeWise pools users’ ETH together and runs validator nodes on behalf of the users. In return, users receive sETH, which represents their share of the pool.
Solana (SOL) Staking
In order to become a validator node on the Solana blockchain and participate in staking, there are several requirements that must be met.
To become a validator node, one must first download and set up the Solana client software. Once the software is installed and configured, the validator node can be activated by depositing SOL into the staking account. The staking account is the account that holds the staked SOL and manages the validator node’s participation in staking.
There is no strict minimum amount of SOL required to run a validator on Solana. However in order to participate in consensus, a vote account is required which has a rent-exempt reserve of 0.02685864 SOL. Voting also requires sending a vote transaction for each block the validator agrees with, which can cost up to 1.1 SOL per day.
The hardware recommendations should be considered bare minimums if the validator is intended to be employed as an RPC node. To provide full functionality and improved reliability, check RPC Node Recommendations.
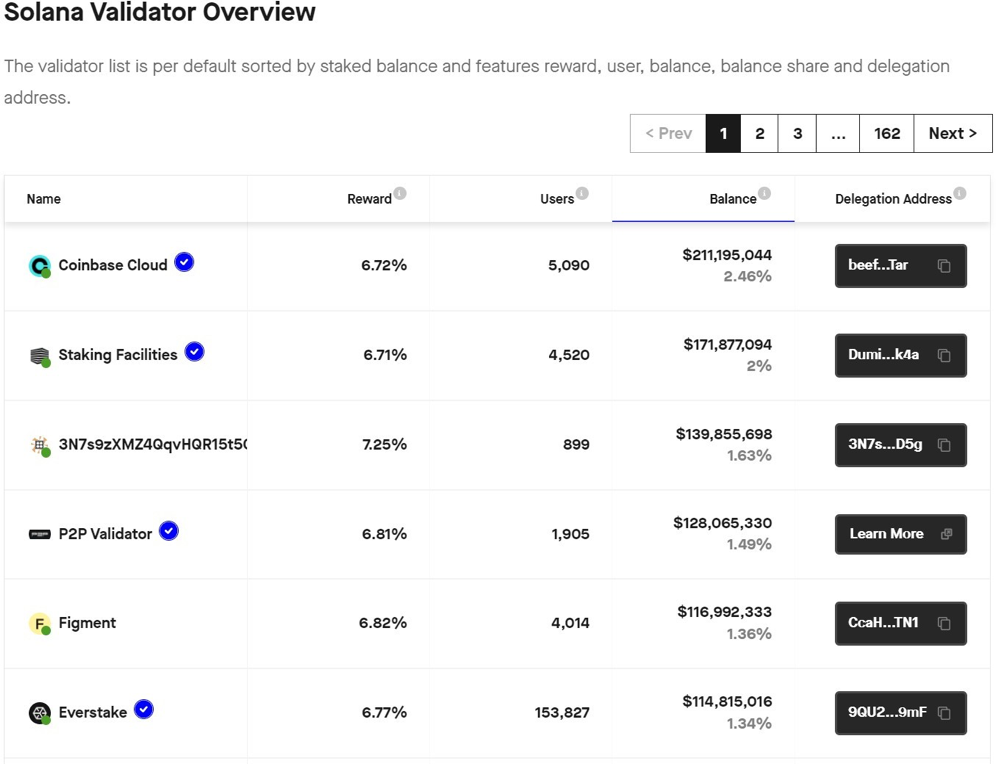
To stake SOL, you can use for example:
- Phantom – It is one of the most popular wallets in the Solana ecosystem. You can choose one among many validators, it is recommended to check and inform yourself on validators.app or StakeView.app to find a ranked list of the best options based on current network conditions.
- Lido – It is a decentralized staking platform that allows users to stake their SOL without having to run their own validator node. Lido operates a network of nodes that are responsible for staking users’ SOL.
Right now, about 2,700,060 SOL with an APR of about 6.6% are in stakes on this platform!
- Marinade Finance – It is a decentralized staking platform that allows users to stake their SOL without having to run their own validator node. Right now, about 4,287,416 SOL with an APR of about 6.54% are in stakes on this platform!
Cosmos (ATOM) Staking
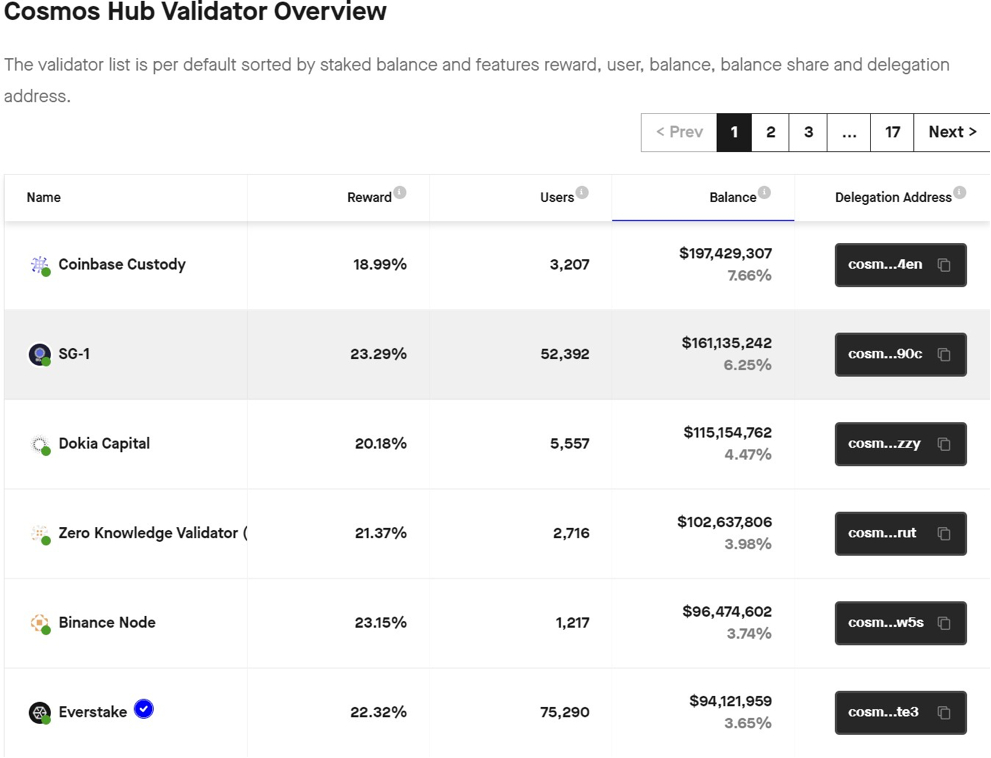
ATOM is a cryptocurrency that powers the Cosmos network, a decentralized network of independent blockchains that can communicate with each other through a hub called the Cosmos Hub. The Cosmos network aims to create an internet of blockchains, allowing different blockchain networks to connect and interact with each other. ATOM holders can participate in staking to secure the network and earn rewards.
On StakingRewards you can read all the data regarding APR and ATOM staked percentage!
To start a node on the Cosmos network, you can read all the specifications on their documentation.
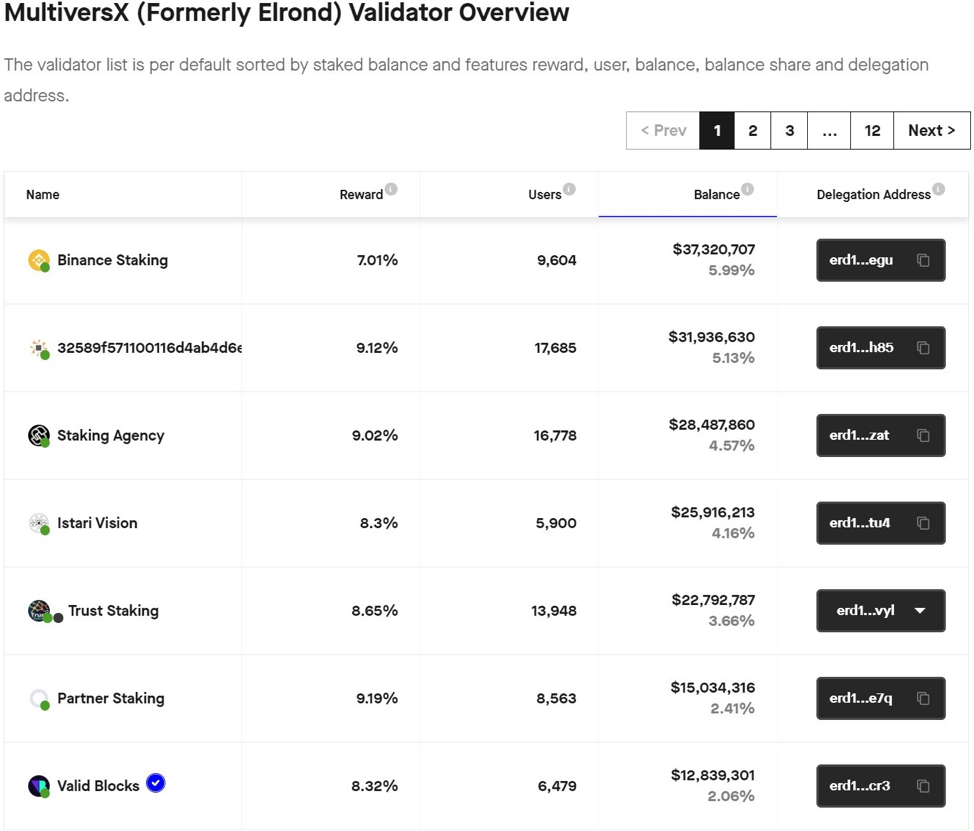
MultiversX (EGLD) Staking
MultiversX is a blockchain PoS that uses sharding as a method to allow the ecosystem to scale.
To open a Staking Agency on the network and allow users to delegate their EGLD, the requirement is to have at least 1250 EGLD and system requirements that you can read about on their developer documents.
To open your own node on the network, however, 2500 EGLD is required and you have to wait for a period in the queue.
The MultiversX network has 3200 validator nodes, but when new nodes want to join, they have to go through a queue. New nodes will be selected in the order in which they are added to the queue.
Whenever one of the 3200 nodes is retired, a new node is selected from the queue, giving everyone a chance to participate in the network.
The MultiversX team owns 675 nodes, but it’s working to promote the decentralization, so they periodically retire some of their own nodes.

An experienced leader in software engineering and technology, I’ve driven value for top-tier Fortune 100 and 500 clients as the former CTO of Big Drop Inc. Overseeing a global team, we secured 34 global awards for pioneering web design using our proprietary tech. As the Co-Founder of Motion Design School, I created an innovative platform for global artists. Now, I apply my expertise to the dynamic world of blockchain, leveraging years of experience to shape decentralized technology’s future.